China is an enormous country, so it should come as no surprise that there are multiple types of spoken Chinese being used — both within its borders and abroad.
Simply referring to the “Chinese language” is too vague; China is home to a multitude of languages and dialects, many of which are mutually unintelligible.
If you are looking for Chinese interpreting services, it is therefore essential that you be specific about the Chinese language or dialect you need interpreted.
Major Variants of Spoken Chinese
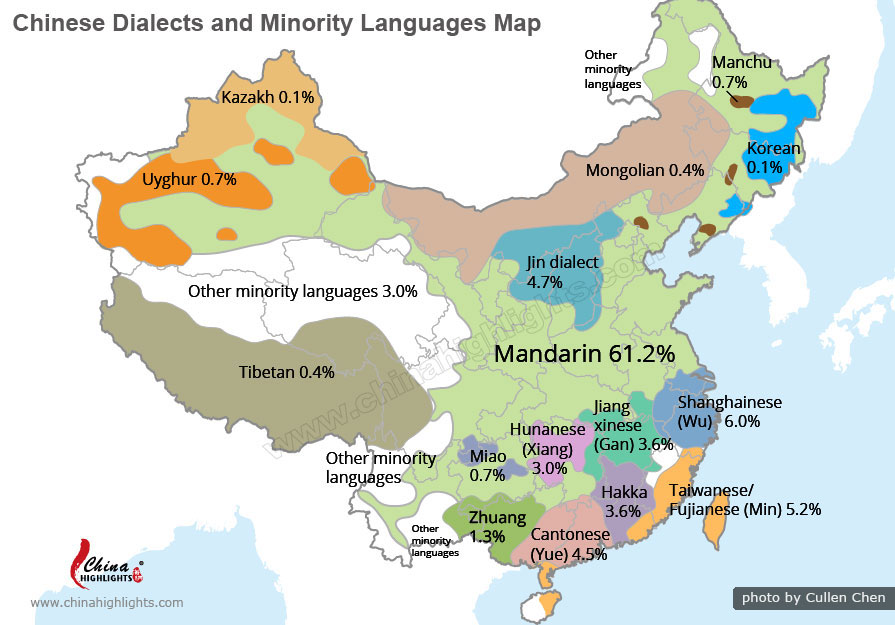
Spoken Chinese languages are among the most commonly used in the world. The best known are undoubtedly Mandarin and Cantonese. Mandarin and Cantonese, although they are often referred to as individual languages, are each technically classified as a dialect of the Modern Standard Chinese language, commonly known as Guoyo or Putonghua.
Mandarin is considered a native language by about two-thirds of China’s inhabitants, making it the most dominant spoken Chinese dialect, while Cantonese lays claim to approximately 55 million speakers in China alone. While these are the spoken Chinese dialects you are most likely to encounter, there are many more!
Spoken Chinese is separated into five main dialectical groups, of which Mandarin is only one. Yue (which includes Cantonese), Min, Wu and Hakka make up the other four, covering more than 200 individual dialects. Some of these dialects are limited to very small geographical areas, while others have speakers all across the country and beyond.
Geography Is Essential to Differences in Spoken Chinese
Just as the Spanish language includes several dialectical differences in different countries and regions around the world, spoken Chinese includes a variety of types that are divided largely along geographical lines. The majority of China’s Cantonese speakers live in the country’s Guangxi and Guangdong provinces — but even within these regions, the dialects of Cantonese can vary. Usually the dialect spoken in Hong Kong is considered the Cantonese point of reference by English speakers.
Mandarin, being the most commonly-used form of spoken Chinese, is more widely distributed throughout China. However, geographical differences are evident even within the Mandarin dialect, which is classified into four groups based on geographical location: Southwest, Southern, Northwestern and Northern Mandarin.
Dealing with Chinese Linguistic Diversity in Interpreting
Chinese language interpreting must always be sensitive to the type of dialect being used.
When seeking interpreting services for spoken Chinese, it’s important to know the dialect for which you need an interpreter. By specifying that you want an expert within a certain dialect of spoken Chinese, like Mandarin or Cantonese, your professional interpreting service will be better able to provide you with a qualified interpreter.
Leave a Reply